An ever-growing role for a tiny lipid
Critical signaling functions have been attributed to phosphatidic acid, or PA, the smallest building block in phospholipid biosynthesis. With a small head group and a net negative charge ranging from -1 to -2 depending on pH, PA can modulate local membrane geometry and recruit a large set of specific proteins to confined membrane subdomains; a recent review by Emeline Tanguy and colleagues summarizes both of these essential actions for PA’s signaling function. PA is versatile and challenging because it can be produced and metabolized by a large set of enzymes.
Although PA is present at low levels in most cell types, it appears to be critical for neuronal and glial cell function. Several neurological diseases maybe attributed, at least in part, to altered PA synthesis and/or catabolism. For example, Ricardos Tabet and colleagues proposed in 2016 that an alteration of the PA/diacylglycerol balance could be a main cause of fragile X syndrome, a genetic cause of intellectual disability. They showed that diacylglycerol kinase-kappa, or DGK-kappa, mRNA was the main target of fragile X mental retardation protein and that reduced DGK-kappa expression impaired PA synthesis in neurons from mice bred not to express FMR1, a protein that male fragile X patients lack. Silencing DGK-kappa in pyramidal neurons from the CA1 region of the hippocampus largely reproduced fragile X symptoms. This PA/DAG imbalance is thus likely to affect DAG and PA downstream signaling required for both maturation of dendritic spines and establishment of correct synaptic plasticity.
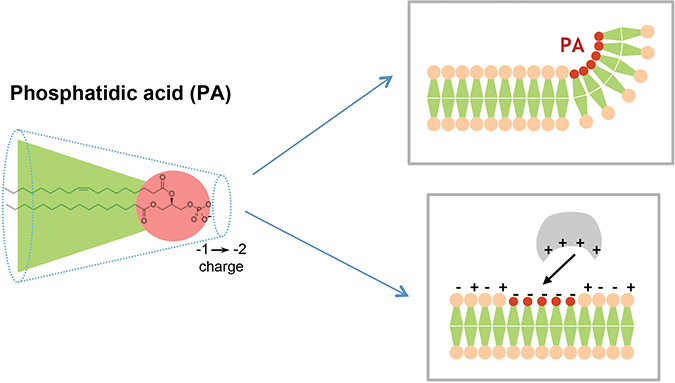 Phosphatidic acid is defined by its shape and charge. This conical lipid generates negative membrane curvature and is negatively charged, thereby recruiting positively charged proteins. Nicolas Vitale
Phosphatidic acid is defined by its shape and charge. This conical lipid generates negative membrane curvature and is negatively charged, thereby recruiting positively charged proteins. Nicolas Vitale
Maria Zeniou–Meyer and colleagues in 2008 proposed that the loss of expression of the kinase RSK2, which leads to Coffin–Lowry syndrome (a rare syndromic form of mental retardation), reduced PA synthesis and distorted neurosecretion. Increased PA synthesis has been reported in gliobastoma, the most frequent and aggressive brain cancer. A link between brain PA levels and Alzheimer’s disease also is starting to emerge, but the exact effects of PA imbalance in neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits has not been identified. Finally, reduced PA synthesis may contribute to fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, as ethanol leads to phospholipase D-mediated phosphatidylethanol production at the expense of PA.
Many cellular pleiotropic functions of PA rely on its ability to regulate actin cytoskeleton dynamics and to modulate membrane-involved functions. The former occurs mainly through PA’s ability to modulate the activity of small GTPases, including Rho and Arf members. The latter probably results both from the original cone shape structure of PA favoring negative membrane curvature and from PA’s net negative charge allowing local recruitment of specific proteins. One remaining challenge is to define precisely sites of PA synthesis within the brain and at the subcellular level in neurons. Recent improvements in lipidomics allow for sensitive quantification of dozens of PA species made with different fatty acids. According to a study by Nawal Kassas and colleagues, the development of novel genetically encoded PA sensors also will be crucial in localizing and potentially quantifying changes in PA and perhaps different PA species.
Despite PA’s low abundance, its relative simplicity, and the complexity of its metabolic and signaling pathways, improved understanding of its multiple functions in brain development and function is now within reach.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

