JLR: A close-up of the lipids in Niemann–Pick disease
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago have used mass spectrometry imaging to map lipid accumulation in Niemann–Pick disease with unprecedented detail. Their results were published in a recent issue of the Journal of Lipid Research.
There are three major forms of Niemann–Pick disease. All are genetic and rare. Type C, or NPC, results in accumulation of cholesterol and complex lipids known as gangliosides in the endosomes and lysosomes of cells. This accumulation leads to neurodegeneration, killing patients when they are young. Many die before they’re 10. It’s rare for one to live to 40.
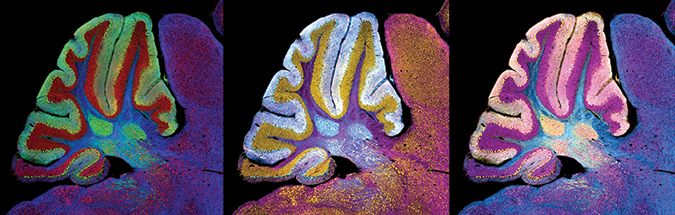 This image of a cerebellum from a mouse with Niemann–Pick C was generated using fluorescence immunolabeling, which is an effective technique for determining protein distribution but cannot capture the location of gangliosides and other lipids that accumulate and cause the disease.Williams/NICHD
This image of a cerebellum from a mouse with Niemann–Pick C was generated using fluorescence immunolabeling, which is an effective technique for determining protein distribution but cannot capture the location of gangliosides and other lipids that accumulate and cause the disease.Williams/NICHD
Based on the way movement and cognition problems emerge in NPC, it seems that different brain regions degenerate at varying stages of the disease. To understand this staging better, it would be useful to visualize lipid accumulation in specific brain regions. This isn’t easy to do with traditional methods, because antibodies against gangliosides are not very specific, so most studies of lipid accumulation in Niemann–Pick disease use homogenized tissue samples from mice with the disease and measure bulk lipids by mass spectrometry.
To achieve greater spatial accuracy, researchers in Stephanie Cologna’s lab used mass spectrometry imaging to look closely at lipids in specific regions of the cerebellum in mice with early-stage NPC. Mass spectrometry imaging, which does not require antibodies or chemical labeling, works by representing small areas of a tissue sample as pixels. The researcher coats a tissue sample in a matrix that helps it to ionize and then collects mass spectra from many tiny areas within that sample.
Each spectrum from one pixel includes information about the abundance of many lipid species. The team used the information about different molecules to make images representing the distribution of lipids across the cerebellum.
Mindful of variations in the intensity of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization spectra that can arise from uneven application of the matrix or variability among samples, the team, led by graduate student Fernando Tobias, also devised an algorithm to evaluate the most abundant signals. The algorithm let them filter out noise and compare measurements of wild-type and NPC brain samples more reliably with many replicates.
Once they compared lipid distributions across the cerebellum, the team made the interesting observation that, while two types of ganglioside (GM2 and GM3) are drastically higher in the NPC mouse’s cerebellum, GM1 seems to go up throughout the brain. Also, GM2 elevation is very tightly localized in a part of the cerebellum called lobule X, but it’s not yet clear what that might mean.
The researchers intend to continue using mass spectrometry imaging to get a more granular picture of the disease course.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

