The many layers of cholesterol regulation
Cholesterol levels in the membranes of animal cells are regulated carefully to remain within narrow limits. Regulation is carried out by a network of proteins that resides in the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, and controls the two pathways by which cells obtain cholesterol: synthesis and uptake from circulating lipoproteins. The key proteins of this network include a cholesterol sensor and a transcription factor. The sensor is Scap, a polytopic ER membrane protein that binds membrane cholesterol. The transcription factor is a domain of another ER membrane protein called sterol regulatory element-binding protein, or SREBP.
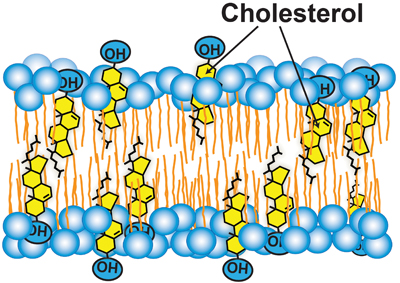 Cholesterol accessibility at the surfaces of membranes rises sharply when its concentration exceeds a threshold, and plays a role in regulating the total cellular level and intracellular distribution of cholesterol. courtesy of Anna Sokolov and Arun Radhakrishnan
Cholesterol accessibility at the surfaces of membranes rises sharply when its concentration exceeds a threshold, and plays a role in regulating the total cellular level and intracellular distribution of cholesterol. courtesy of Anna Sokolov and Arun Radhakrishnan
When ER cholesterol is low, Scap initiates a series of molecular events that eventually release SREBP’s transcription factor domain into the cytosol so it can travel to the nucleus to upregulate genes for cholesterol synthesis and uptake. When ER cholesterol rises above a threshold, Scap binds cholesterol and undergoes a conformation change that blocks the processing of SREBPs. Thus, Scap spearheads a feedback mechanism that ensures rapid adjustments to changes in cellular cholesterol levels to ensure cholesterol homeostasis.
However, the cellular distribution of cholesterol poses a significant challenge to this feedback mechanism. Seventy to 90 percent of the cell’s cholesterol is located in the plasma membrane, or PM, whereas Scap is in the ER, which contains only about 1 percent of the cell’s cholesterol. If Scap is to execute its sensing function, the cholesterol-poor ER must be in constant communication with the cholesterol-rich PM so it can be notified promptly of changes in cholesterol levels. Without such a link, Scap would be blind to changes in cellular cholesterol. Indeed, disrupting this link through the use of a toxin that sequesters cholesterol in the PM results in a lowering of ER cholesterol even though PM cholesterol is unchanged. In response to this artificial induction, Scap activates SREBPs even though cellular cholesterol has not been depleted.
How are cholesterol levels in ER linked to those in PM? This process requires mechanisms to transport hydrophobic cholesterol across the aqueous cytosol and mechanisms to regulate these transport pathways. Cholesterol transport likely involves a combination of vesicular, nonvesicular and membrane contact site-mediated pathways, and remains poorly understood. We know a little more about how this transport may be regulated. Recent work has used soluble cholesterol-binding toxins to assay the exposure of cholesterol at the surface of purified PMs. These studies revealed that PM cholesterol was sequestered in the membrane bilayer and inaccessible to toxins until it exceeded a threshold concentration of about 35 mole percent of total PM lipids. Above this sharp threshold, PM cholesterol was accessible to bind to toxins. Sharp changes that have been observed for the exposure of PM cholesterol to the enzyme cholesterol oxidase may occur at similar thresholds.
It is tempting to speculate that intracellular cholesterol transport pathways are also sensitive to a sharp change in accessibility of cholesterol on the cytoplasmic leaflet of the PM, allowing for transport to ER to occur only after the PM’s cholesterol needs have been satisfied. How subthreshold levels of cholesterol are sequestered in the PM to prevent interactions with the intracellular transport machinery remains a mystery. We have learned a lot, but there are many more layers of cholesterol regulation yet to be revealed.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

