JBC: Researchers decipher how barbiturates work
Modern medicine would be unthinkable without the use of anesthesia during surgical procedures. In a recent paper in the Journal of Biological Chemistry that was selected as one of the Editors’ Picks, Marc Delarue of the Pasteur Institute in France and colleagues solved how a class of drugs called barbiturates function to induce anesthesia. “This work describes, for the first time, the three-dimensional structure by X-ray crystallography of barbiturates bound to the target receptor,” says Zaineb Fourati, one of the first authors on the paper. She adds, “Understanding the mechanism underlying anesthetics’ action is the first step toward the conception of better ones that are more specific and with less side effects.”
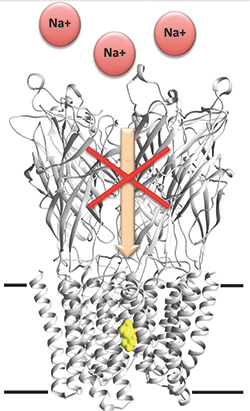 Researchers unveil barbiturates’ mechanism of action.IMAGE COURTESY OF MARC DELARUE
Researchers unveil barbiturates’ mechanism of action.IMAGE COURTESY OF MARC DELARUE
Barbiturates, a class of drugs derived from barbituric acid, made their debut in Germany in 1903. Their name is thought to be a fusion of “Barbara” and uric acid, a component of urine. Sources are divided on which female inspired the name, who could have been St. Barbara or someone less than a saint.
The first commercially available form of barbiturates was marketed as sleeping pills. Other medical applications of barbiturates soon emerged, including as anesthetics, sedatives and anticonvulsants, which led to their widespread use in the first half of the 20th century. However, the side effects of barbiturates led to their regulation and decreased popularity.
“Uncontrolled use of barbiturates could have hazardous consequences, from addiction to death by overdose,” says Fourati. “One concrete example is the presumably intentional death of the famous Marilyn Monroe due to a barbiturate overdose in the early 1960s.” Nevertheless, barbiturates remain essential in the treatment of epilepsy and as an intravenous general anesthetic.
Anesthetics act by decreasing the relay of information in the nervous system. Specifically, anesthetics affect several types of membrane-embedded ion channels. The principal targets of barbiturates are thought to be anionic and cationic pentameric ligand-gated ion channels, known as pLGICs. Although there is some evidence to show that barbiturates bind to the cylindrical pore of the ion channel, the exact nature of this interaction is unclear.
To understand this interaction better, Delarue and colleagues used the bacterial pH-gated receptor GLIC, which has high structural similarity to mammalian pLGICs. They first showed that the bacterial version of the channel behaved much like its eukaryotic counterpart by demonstrating that a specific barbiturate called pentobarbital can inhibit the electrical current of the bacterial GLIC channel.
Next, the investigators used three barbiturate derivatives — bromobarbital, thiopental and selenocyanobarbital — that were modified chemically such that they displayed an unusual electron scattering behavior to help assign bound ligands in the X-ray structure unambiguously. The investigators showed that all three barbiturate derivatives bound to the closed GLIC channel deep within the central pore, and they used computational simulations of the channel in open and desensitized states to support their findings further.
“This work partly reveals how barbiturates induce anesthesia,” says Fourati. “As these drugs act on the nervous system, it is very important to address the exact mechanism of their action, and the structure provides a direct proof of a molecule binding to a given site.”
She and her colleagues think that the knowledge gained in this study can help design a new generation of barbiturates not only for anesthesia but also for psychiatric and neurological disorders.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Life in four dimensions: When biology outpaces the brain
Nobel laureate Eric Betzig will discuss his research on information transfer in biology from proteins to organisms at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Fasting, fat and the molecular switches that keep us alive
Nutritional biochemist and JLR AE Sander Kersten has spent decades uncovering how the body adapts to fasting. His discoveries on lipid metabolism and gene regulation reveal how our ancient survival mechanisms may hold keys to modern metabolic health.

Redefining excellence to drive equity and innovation
Donita Brady will receive the ASBMB Ruth Kirschstein Award for Maximizing Access in Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Mining microbes for rare earth solutions
Joseph Cotruvo, Jr., will receive the ASBMB Mildred Cohn Young Investigator Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Fueling healthier aging, connecting metabolism stress and time
Biochemist Melanie McReynolds investigates how metabolism and stress shape the aging process. Her research on NAD+, a molecule central to cellular energy, reveals how maintaining its balance could promote healthier, longer lives.

Mapping proteins, one side chain at a time
Roland Dunbrack Jr. will receive the ASBMB DeLano Award for Computational Biosciences at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

