Chronic fatty liver disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD, and its progressive form, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, have emerged as significant public health concerns in Western societies. NAFLD is a continuum of chronic fatty liver diseases ranging from benign hepatic steatosis to NASH, which consists of fatty liver with inflammation and injury. NASH can progress to severe fibrosis or cirrhosis, and primary hepatocellular cancer, or HCC. The increase in NAFLD in adults and children over the last 20 years parallels the obesity epidemic in Western societies. Factors contributing to the increased incidence of NAFLD include a sedentary lifestyle and poor diet of fat, simple sugar and cholesterol.
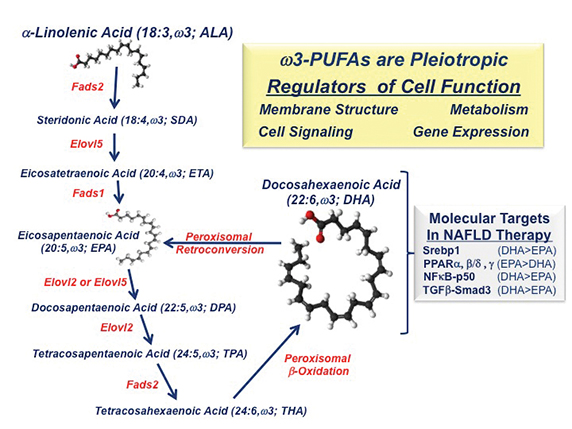 IMAGE COURTESY OF DONALD B. JUMP
IMAGE COURTESY OF DONALD B. JUMP
Since there are no U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs for NASH treatment, current therapies rely on lifestyle modification and treatment of the comorbidities associated with NAFLD, including obesity, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Several clinical studies have evaluatedomega-3 fatty acids in NAFLD therapy, because omega-3 fatty acids have been reported to augment fatty-acid oxidation and triglyceride catabolism and suppress fatty-acid synthesis, inflammation and blood levels of triglycerides. Moreover, humans and mice with NAFLD have low hepatic omega-3 and omega-6polyunsaturated fatty acid, or PUFA content, when compared with healthy individuals (See Depner, C. M. et al 2013 and Arendt, B. M. et al 2015).
Most clinical studies use a mix of eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5 EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6 DHA) and report that these dietary lipidslower liver fat but do not reduce liver fibrosis, a risk factor for cirrhosis and HCC. In contrast, NAFLD patients consuming EPA have no reduction in hepatic fat or fibrosis. Studies of mice with NASH that lack the low-density lipoprotein receptor, or LDLR -/- have shown that DHA, but not EPA, reduces Western dietinduced fatty liver, inflammation and fibrosis (See Depner, C. M. et al 2013 and Lytle, K. A. et al 2015).
The differential action of C20–22 omega-3 fatty acids on clinical outcomes can be explained, at least in part, by effects on fatty-acid metabolism and differences in the molecular actions of EPA versus DHA. DHA and EPA inhibit fatty-acid synthesis by suppressing the nuclear abundance of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1, a transcription factor controlling the expression of enzymes involved in de novo lipogenesis and PUFA synthesis. As such, humans and mice consuming EPA alone show no significant increase in blood or hepatic DHA content (See Depner, C. M. et al 2013 and Itakura, H. M. et al 2011). DHA consumption, however, increases blood and hepatic DHA, EPA and the longchain n-3 fatty acid docosapentaenoic acid, or DPA. EPA and DPA increase through retroconversion.
Dietary DHA, but not EPA, attenuates Western diet-induced nuclear accumulation of transcription factors involved in inflammation, such as NF-kappa B, and fibrosis, such as phospho-Smad3. While NF-kappa B controls the expression of multiple inflammatory factors, including Cox2,chemokines and cytokines, phospho-Smad3 is a downstream mediator of TGF-beta signaling. TGF-beta is a major regulator of hepatic stellate cellfunction and fibrosis. The impact of DHA on mouse liver fibrosis is TGF-beta receptors, factors regulating TGF-beta signaling, collagensubtypes, and enzymes involved in protein crosslinking and extracellular matrix remodeling.
Together, these studies establish that DHA controls several transcriptional regulatory networks relevant to NAFLD. There remain, however, several unanswered questions. Chief among these is determining why the mix of EPA and DHA fails to affect hepatic fibrosis in humans significantly. It will require more investigation to understand how omega-3 PUFA control pathways linked to chronic fatty liver disease.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

