JLR: Using microRNAs to target cancer cells
Lipids form the membranes of our cells and serve as rainy day fuel. However, cancer cells have a habit of dysregulating every possible pathway they can, including lipid metabolism, generating an overabundance of lipids. Fortunately, the body already produces molecules that have the potential to stop this dysregulation in its tracks: microRNAs.
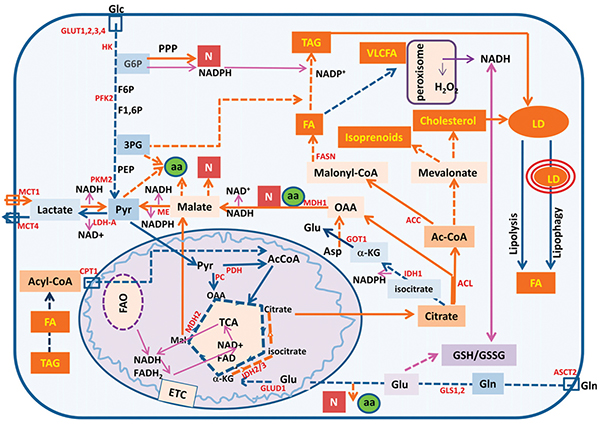 Summary of the metabolic pathways altered in cancer that are described in this review
Summary of the metabolic pathways altered in cancer that are described in this review
In a recent review in the Journal of Lipid Research, Marta Gómez de Cedrón and Ana Ramírez de Molina of the Madrid Institute of Advanced Studies delve into exactly which microRNAs can be used to target cancer cells.
Lipids, molecules known for their insolubility in water, are synthesized to provide membrane integrity and are signaling molecules used by downstream effectors in the cell. As an energy source, lipids are broken down via beta-oxidation, and the intermediates can be used in other metabolic pathways.
MicroRNAs, meanwhile, are small single-stranded RNA molecules that can stop the synthesis of proteins. They bind to mRNA transcripts in the cell and cause their degradation, preventing production of proteins that cancer cells so desperately need.
The authors of the JLR review discuss several lipid-metabolism enzymes that cancer cells rely on whose targeting could prevent the synthesis and dissemination of lipids altogether. For example, an enzyme called fatty acid synthase, which is involved in the making of lipids, is upregulated and overused in cancer cells. Activation of a microRNA targeting this gene may shut down production of this enzyme and turn off this essential pathway. Mono-acyl glycerol lipase, which is involved in storing these lipids, may also be targeted.
Why is all of this important? If researchers can use normal cells’ machinery to target cancer cells specifically, the cancer may be slowed or completely halted. In fact, scientists have used antisense oligonucleotides that bind to microRNAs and repress their action as well as primary microRNAs, which mimic RNA of choice and activate their function. These methods have been used as cancer therapy in clinical trials.
MicroRNAs stand out from conventional gene-therapy-based approaches and have a niche in lipid metabolism. They can be designed specifically to target a gene and serve as modulators rather than on/off switches. Increased lipid formation and breakdown in cancer cells creates vulnerability that might be taken advantage of by microRNAs. In addition, cancer as a whole involves a combination of many factors, and microRNAs could lead the attack as professional pathway regulators to reset the normal metabolic landscape.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Sizing up cells: How stem cells know when to divide
Stanford University researchers find that stem cells control their size early in cell division across living multicellular systems.

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

