From the journals: MCP
Understanding the stages of mitophagy. Defining subcellular localization. Read about papers on these topics recently published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Working from the outside in
As cells adjust to the stresses of life, mitochondria also must adapt. Over time, mitochondria get damaged and then recycled by a specialized autophagy process called mitophagy.
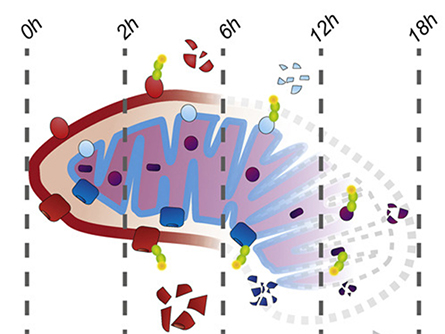
in during mitophagy.
During mitophagy, proteins are marked for degradation through ubiquitination. Phosphorylation works in tandem with ubiquitination, as each modification can provide positive or negative feedback for the other. In particular, mitophagy requires the E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin and the serine/threonine-protein kinase PINK1. Researchers have identified mutations in both enzymes in Parkinson’s disease, so understanding their function is critical.
Despite an abundance of literature, scientists still have key questions about the process of mitophagy. Some researchers have demonstrated that autophagosomes consume mitochondria all at once during mitophagy, although others suggest individual sections within the mitochondria can be broken down piece by piece.
In a recent paper published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Katharina I. Zittlau and colleagues at the University of Tübingen describe using a three-tiered proteomic approach to examine parkin-dependent mitophagy in HeLa cells. After inducing mitophagy, the team quantified total protein levels over 18 hours to evaluate mitochondrial protein degradation in the presence or absence of functional parkin. They also measured changes in protein ubiquitination and phosphorylation.
Their data support an outside–in breakdown of mitochondria during mitophagy, showing evidence for the ubiquitination and degradation of proteins in the outer mitochondrial compartments first, with the inner compartments following later. Using a vast data set, the researchers also identified examples in which a phosphorylation event blocked or enhanced ubiquitination during mitophagy. In particular, they showed that dephosphorylation of voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 is required for its parkin-dependent ubiquitination and ultimate degradation.
This study provides detailed information that enhances our knowledge of mitophagy as well as the specific contribution of parkin to each stage of the process.
Mapping the cell
The cytoplasm is a densely packed yet well-organized space. A multitude of biochemical reactions occur simultaneously, each localized to a specific domain, such as inside the nucleus, on the mitochondrial surface or at the plasma membrane. As a result, the localization of RNA and proteins — as well as the intracellular trafficking to their final destination — must be tightly regulated. Disruption of this spatial organization can be problematic, as numerous diseases are characterized by mislocalized proteins.
Although researchers can gain a wealth of knowledge from global transcriptomic and proteomic data sets, the story is incomplete without spatial information. Local enrichment or depletion of macromolecules — often masked in whole-cell omics — regulates these biological pathways and, ultimately, cell function.
Josie A. Christopher and a team from the University of Cambridge recently published a comprehensive review of methods used to study the subcellular localization of proteins and RNA in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. The authors provide a detailed overview of techniques such as microscopy-based assays, imaging mass cytometry, and coupling proteomics/transcriptomics with biochemical fractionations or proximity labeling. The advantages and limitations of each are discussed to help readers select the best methods for their own projects.
The techniques highlighted in this review will be crucial in answering basic questions about cellular organization as well as leading the way for translational research and new diagnostic approaches.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Decoding microglial language
Emory University scientists characterize extracellular vesicles that facilitate intercellular communication.

What is metabolism?
A biochemist explains how different people convert energy differently – and why that matters for your health.

What’s next in the Ozempic era?
Diabetes, weight loss and now heart health: A new family of drugs is changing the way scientists are thinking about obesity — and more uses are on the horizon.
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.

