JBC: New insights into the molecular weapons of the plant microbiome
Like all organisms, plants are associated with bacterial communities in which helpful and harmful bacteria compete for dominance. Among the weapons of these warring bacteria are molecular syringes that some bacteria can use to inject toxins into others. In a study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, researchers at McMaster University in Canada pinpointed the identity of one such toxin used by a soil-dwelling bacterium that protects plants from disease.
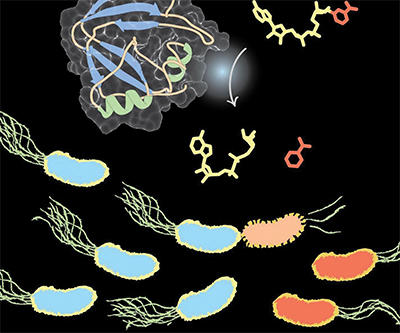 The NAD-degrading enzyme Tne2 is secreted through the type VI secretion system of the plant-protective bacterium Pseudomonas protegens.Courtesy of John Whitney/McMaster University
The NAD-degrading enzyme Tne2 is secreted through the type VI secretion system of the plant-protective bacterium Pseudomonas protegens.Courtesy of John Whitney/McMaster University
The bacterium Pseudomonas protegens can kill soil-dwelling plant pathogens, including fungi and bacteria, that attack the roots of important crops such as cotton. P. protegens releases diverse antimicrobial compounds into the soil, but John Whitney was curious specifically about the compounds that it was injecting directly into other bacteria through the type VI secretion system, or T6SS.
The T6SS “is this molecular nanomachine that injects toxic protein into other species of bacteria and kills them,” Whitney said. “Plant protective bacteria that have (T6SS) can protect plants from pathogens better relative to (bacteria) that don’t have it.”
Jenny Tang and Nathan Bullen, undergraduate students from the University of Waterloo working with Whitney on a co-op work-study assignment, spearheaded the discovery that the toxic protein used by P. protegens against other bacteria acts on a molecule found in nearly all living cells: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+.
NAD+ is a cofactor, or “helper” molecule, in many biochemical reactions. By injecting a protein that destroys NAD+, P. protegens is able to kill other bacteria.
The team then investigated the genome sequences of hundreds of other bacteria to see how widespread the strategy of targeting NAD+ is in microbial warfare. They found that many bacteria with secretion systems carry genes similar to the one encoding the NAD-targeting toxin.
“We started to see that this isn’t just a way of killing that is enacted by plant-protective bacteria,” Whitney said. “If you look at the distribution of this (protein) among all sequenced bacteria, it appears that many different bacteria in many different environmental niches use this mode of action to outcompete other bacteria.”
The abundance of these toxins in nature raises questions: How do different bacteria in different environments evolve to resist this toxin? Are NAD-targeting toxins more effective against some bacterial species than others? Understanding the diversity of bacterial weapons is an active area of study among agricultural researchers who would like to develop better ways to fight plant diseases.
“The identification and characterization of antibacterial toxins produced by plant-protective bacteria may one day allow us to engineer these bacteria to have enhanced ability to suppress pathogens,” Whitney said.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.
From the journals: JLR
How lipogenesis works in liver steatosis. Removing protein aggregates from stressed cells. Linking plasma lipid profiles to cardiovascular health. Read about recent papers on these topics.
Small protein plays a big role in viral battles
Nef, an HIV accessory protein, manipulates protein expression in extracellular vesicles, leading to improved understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis.

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.

.jpg?lang=en-US&width=300&height=300&ext=.jpg)