Exercise and fatty food: Using plasma proteomics to understand obesity
During the COVID-19 pandemic, one of Western society’s greatest health problems has continued its decades-long rise: obesity. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, obesity rates nearly tripled from 1962 to 2016 (from 14% to 40%), with obesity-related health care costs now likely over $150 billion annually. While the effects of obesity are easy to see, our understanding of its underlying physiology continues to evolve.
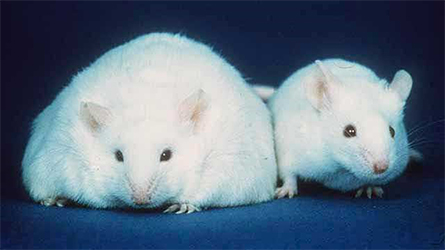
highlighting how exercise can prevent high fat diet–induced changes in protein
levels could provide new tools in the fight against obesity.
“Unfortunately, obesity is at epidemic levels in our communities,” Stephen Twigg, an endocrinologist at the University of Sydney, said. “Methods to prevent it, let alone treat it, are still quite lacking.”
Twigg and University of Sydney biochemist Mark Larance, along with an international team of scientists, have sought to characterize the interplay of two key obesity triggers. High-fat diets, or HFD, and lack of exercise both have been implicated in obesity; however, their effect on the plasma proteome (the milieu of soluble proteins within an organism) has not been well characterized. In a paper recently published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Larance and Twigg compared mice fed an HFD to those fed a normal diet and subjected to various exercise regimens to elucidate their combined effect on the plasma proteome.
Following 10 weeks on an HFD, nearly 40% of detected plasma proteins in the mice showed changes. These changes were primarily in liver-associated proteins such as aldolase B, or ALDOB (a key sugar-metabolizing enzyme), a finding consistent with the prevalence of liver damage in obese mice and humans. For mice where these changes already had occurred, exercise as treatment after the fact provided little benefit: Only two of the 82 changed proteins were returned to pre-HFD levels. However, in mice that exercised concurrently with the HFD, roughly 20% of the proteins that were altered in the nonexercising mice maintained their healthy baselines. These effects were independent of the type of exercise, with both endurance and high-intensity interval exercise showing similar results.
“This is one of the first unbiased analyses of the response to HFD,” Larance said. “A lot of those changes, we couldn’t have predicted what they would be. I’ve got the feeling that there are definitely proteins in the plasma that are being ignored at the moment that could be more sensitive than some of the current markers of liver damage … For example, ALDOB might be a more sensitive measure (than current clinical markers) both in humans and in mice.”
Despite these exciting discoveries, significant questions remain. “From the most abundant protein to the least abundant protein spans 13 orders of magnitude,” Larance said, noting the difficulty in detecting low-concentration but important protein species. The type of HFD also heavily influences outcomes, with proteins behaving differently based on the types of fats and number of calories eaten. Additionally, as with any study in mice, differences between the specific changes seen in them and in humans are likely.
Despite these limitations, Larance and Twigg’s work provides a significant advance in our understanding of the proteomics of obesity, and if nothing else, as Twigg concluded, “Probably much better to do some exercise rather than none.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Weedy rice gets competitive boost from its wild neighbors
Rice feeds the world. But researchers have found that a look-alike weed has many ways of getting ahead.

From the journals: JLR
A “T” makes a difference in blood clotting. High cholesterol: two screens are better than one. Biomarkers for cardiovascular risk. Statin-induced changes to the HDL lipidome. Read about recent papers on these topics.

Decoding microglial language
Emory University scientists characterize extracellular vesicles that facilitate intercellular communication.

What is metabolism?
A biochemist explains how different people convert energy differently – and why that matters for your health.

What’s next in the Ozempic era?
Diabetes, weight loss and now heart health: A new family of drugs is changing the way scientists are thinking about obesity — and more uses are on the horizon.
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.

