Fishing for enzymes deep in the ocean
When a research team pulls up a trawling net from the ocean floor, researchers often scramble to douse the specimens in ethanol or formaldehyde. It’s important to prevent decay of organisms that usually die before they even reach the surface. But Anderson Garbuglio de Oliveira, a chemist studying marine bioluminescence, would rather they were frozen.
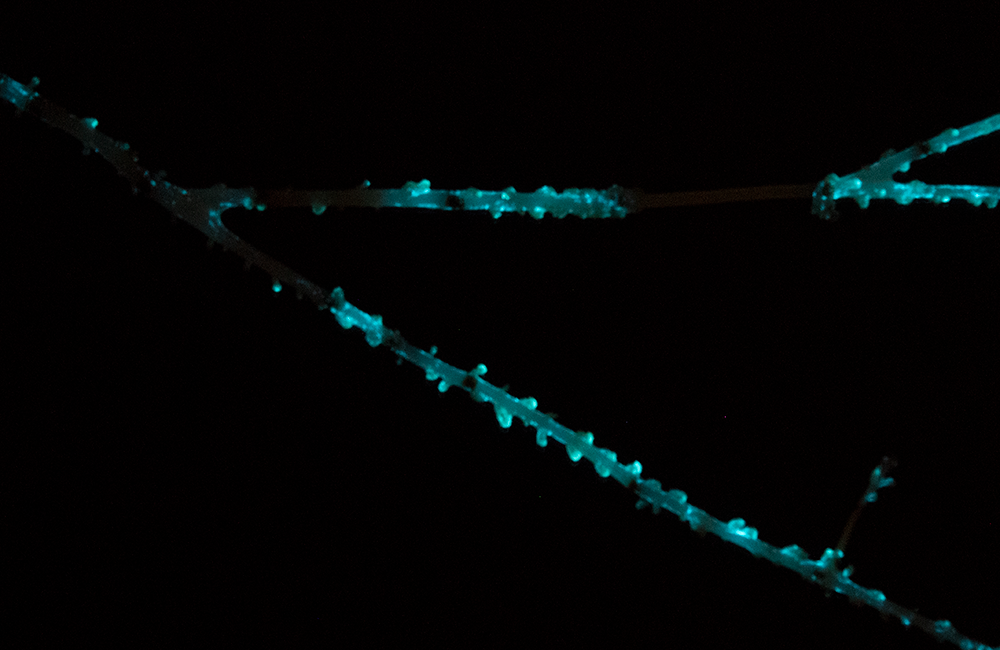
“If you throw a net in the ocean, you will probably find a lot of bioluminescent organisms,” he said. About 90% of deep sea species produce light; but that glow is almost invisible in bright daylight, and his shipboard colleagues are usually interested in other topics. To retrieve and freeze bioluminescent tissue samples before they are pickled in formaldehyde, he said, “I must be very quick.”
Back in the lab at the University of Sao Paulo, Oliveira’s research team investigates the activity of luciferase enzymes, which produce light through a reaction between oxygen and a family of substrate molecules. While some luminescence systems, such as those from comb jellies, are well understood, working with other organisms, such as segmented worms, is “very, very difficult,” Oliveira said, “because their systems are completely new. … Most of the time you have no idea what you’re dealing with.”
Biotechnologists have found numerous laboratory uses for the best-known luciferases, which come from jellies and fireflies. Still, surprisingly little is known about the other biochemical systems that produce light, a phenomenon that evolved on at least 94 independent occasions.
Oliveira is looking for enzymes with properties that could be biochemically interesting and lead to novel uses, such as detecting magnesium or calcium without needing to use fluorescence microscopy. He said, “You can find a lot of interesting things in these weird animals.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.
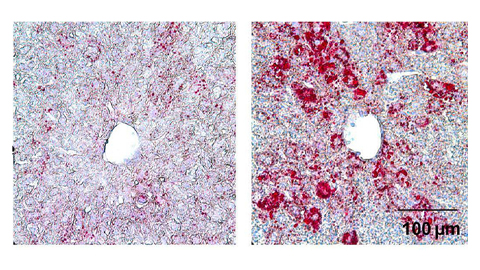
From the journals: JLR
How lipogenesis works in liver steatosis. Removing protein aggregates from stressed cells. Linking plasma lipid profiles to cardiovascular health. Read about recent papers on these topics.
Small protein plays a big role in viral battles
Nef, an HIV accessory protein, manipulates protein expression in extracellular vesicles, leading to improved understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis.

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.

