Researchers retool genomics labs
to provide COVID-19 testing
Researchers at San Francisco’s Innovative Genomics Institute announced today that they are opening a COVID-19 testing center that will provide at least 1,200 tests each day for patients in San Francisco. The IGI is one of several academic institutes whose laboratories are switching focus to contribute to the COVID-19 response.

Labs that conduct high-throughput genome sequencing at IGI, Boston’s Broad Institute and San Francisco’s Chan-Zuckerberg Biohub have retooled recently to provide clinical testing for SARS-nCoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. These overhauls by volunteer scientists and administrators are adding capacity for thousands of tests and rapid turnaround time to help public health departments determine how many people are infected.
Jennifer Doudna, a professor at the University of California Berkeley and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator, founded and leads the IGI.
“Imagine setting that up — a process that would normally take months to years — in a couple weeks. It’s really extraordinary,” Doudna said in an IGI press release.
Doudna and colleague Fyodor Urnov, also a UC Berkeley professor and a technical director at the IGI, put out a call for volunteers in mid-March after hearing about the diagnostic testing effort at the neighboring Biohub. Within hours, 800 members of San Francisco’s biomedical research community, mainly graduate students and postdocs, responded.
Jenny Hamilton, a postdoctoral fellow in Doudna’s UC Berkeley lab, led the technical team that transformed the genomics core into a clinical testing laboratory, and validated the test results, in just two weeks.
“The room that we’re using was previously part of a genomics core facility on campus, and because of that it had some robotics for high-throughput experiments already installed,’ Hamilton said. “Because the campus is shut down and nobody’s doing high-throughput sequencing experiments right now, we’ve been able to quickly reconfigure the room.”
Using liquid-handling robots and reagents bought and donated from multiple sources, Hamilton and her team set up and validated a mostly automated pipeline for extracting RNA from patient samples and conducting a standard reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, or RT-PCR, assay for SARS-nCoV-2. Advisers from industry helped the researchers program the robotic pipeline.
Some widely used reagents, such as disinfectant and qPCR master mix, have been difficult to come by. According to Alexandra Amen, another postdoc in the Doudna lab who helped run the lab-conversion effort, “The hardest thing is sourcing materials that are in low supply.”
As testing gets underway, volunteer researchers will operate the diagnostic lab, testing samples collected from patients at UC Berkeley’s medical center and other hospitals in San Francisco’s East Bay. They hope to return results of 1,200 to 4,000 tests daily within 24 hours, improving on turnaround times that Kaiser Health News reports can take three days to a week. As for funding, the team said through a spokesperson, “We hope to fund the IGI’s testing lab through donations to enable us to serve those without insurance.”
Ordinarily, the institute focuses on genome engineering. Its research programs work to isolate new CRISPR systems from microbes, improve genome editing tools, genetically engineer crops and diagnose human diseases.
“All of our laboratories do PCR every day,” Doudna stated in the IGI release. “But for this test we need to go above and beyond to ensure we can provide accurate detection.”
Researchers didn’t know initially whether the effort was entirely legal. Clinical laboratories must be licensed by state and federal governments to ensure that they report valid results. But given the COVID-19 public health emergency, the IGI release stated, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the California Department of Public Health have relaxed some restrictions on who may test for and report new cases of the novel coronavirus.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.
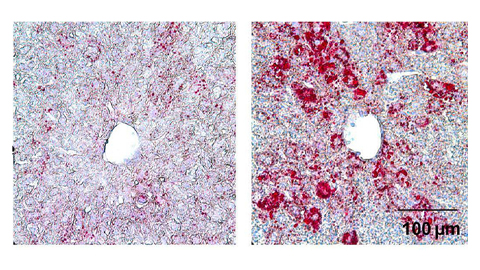
From the journals: JLR
How lipogenesis works in liver steatosis. Removing protein aggregates from stressed cells. Linking plasma lipid profiles to cardiovascular health. Read about recent papers on these topics.
Small protein plays a big role in viral battles
Nef, an HIV accessory protein, manipulates protein expression in extracellular vesicles, leading to improved understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis.

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.

