JLR: Using microRNAs to target cancer cells
Lipids form the membranes of our cells and serve as rainy day fuel. However, cancer cells have a habit of dysregulating every possible pathway they can, including lipid metabolism, generating an overabundance of lipids. Fortunately, the body already produces molecules that have the potential to stop this dysregulation in its tracks: microRNAs.
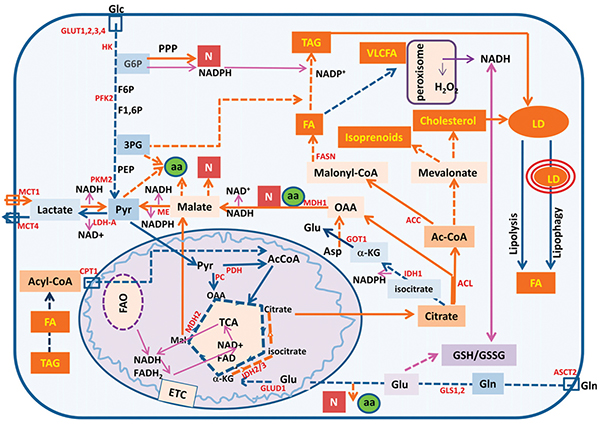 Summary of the metabolic pathways altered in cancer that are described in this review
Summary of the metabolic pathways altered in cancer that are described in this review
In a recent review in the Journal of Lipid Research, Marta Gómez de Cedrón and Ana Ramírez de Molina of the Madrid Institute of Advanced Studies delve into exactly which microRNAs can be used to target cancer cells.
Lipids, molecules known for their insolubility in water, are synthesized to provide membrane integrity and are signaling molecules used by downstream effectors in the cell. As an energy source, lipids are broken down via beta-oxidation, and the intermediates can be used in other metabolic pathways.
MicroRNAs, meanwhile, are small single-stranded RNA molecules that can stop the synthesis of proteins. They bind to mRNA transcripts in the cell and cause their degradation, preventing production of proteins that cancer cells so desperately need.
The authors of the JLR review discuss several lipid-metabolism enzymes that cancer cells rely on whose targeting could prevent the synthesis and dissemination of lipids altogether. For example, an enzyme called fatty acid synthase, which is involved in the making of lipids, is upregulated and overused in cancer cells. Activation of a microRNA targeting this gene may shut down production of this enzyme and turn off this essential pathway. Mono-acyl glycerol lipase, which is involved in storing these lipids, may also be targeted.
Why is all of this important? If researchers can use normal cells’ machinery to target cancer cells specifically, the cancer may be slowed or completely halted. In fact, scientists have used antisense oligonucleotides that bind to microRNAs and repress their action as well as primary microRNAs, which mimic RNA of choice and activate their function. These methods have been used as cancer therapy in clinical trials.
MicroRNAs stand out from conventional gene-therapy-based approaches and have a niche in lipid metabolism. They can be designed specifically to target a gene and serve as modulators rather than on/off switches. Increased lipid formation and breakdown in cancer cells creates vulnerability that might be taken advantage of by microRNAs. In addition, cancer as a whole involves a combination of many factors, and microRNAs could lead the attack as professional pathway regulators to reset the normal metabolic landscape.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

What is metabolism
A biochemist explains how different people convert energy differently – and why that matters for your health.

What’s next in the Ozempic era
Diabetes, weight loss and now heart health: A new family of drugs is changing the way scientists are thinking about obesity — and more uses are on the horizon.
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.
From the journals: JLR
How lipogenesis works in liver steatosis. Removing protein aggregates from stressed cells. Linking plasma lipid profiles to cardiovascular health. Read about recent papers on these topics.

