How Salmonella runs hot and cold
“Don’t eat raw cookie dough!” is something adults often say to children. One reason we wash vegetables, cook meat and — usually — don’t eat raw cookie dough is to avoid getting infected with pathogens like Salmonella.
As familiar as the name of this bacteria is, there’s quite a bit we don’t know about how it grows and spreads. One thing complicating our understanding is that Salmonella survives in disparate conditions. We have a handle on its life when it gets into our bodies, but it also must survive on crops in cooler outdoor temperatures and even in the fridge.
Researchers in Osnabrück, Germany, recently published a study in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics about how the Salmonella proteome changes under different temperatures and nutrient conditions, opening the door to developing more efficient prevention techniques.
To understand how Salmonella survives, they grew it at temperatures from about as cold as a refrigerator up to as warm as a human body. They also varied the available nutrients. Then, after monitoring growth rate and other factors, they collected samples from all the growth conditions, extracted the proteins and analyzed them by mass spectrometry to get a picture of each one’s entire proteome.
They found tons of data, which they’ve made available for other researchers, and started characterizing it with broad strokes. More pathogenic factors were expressed at body temperature. Heat and cold stress response proteins changed across the conditions, as did proteins regulating gene expression and metabolism: Glycolysis enzymes are less abundant at colder temperatures, so the Salmonella may be upregulating their citric acid cycle to compensate.
When looking at the proteomic data for the cooler temperatures, they made unexpected finds, according to first author Laura Elpers. “It was a surprise to identify flagella,” the long thin structures bacteria use like a propeller for locomotion, she said.
In E. coli, another common foodborne pathogen, flagella are expressed only at body temperature, not colder temperatures, and researchers thought it would be the same for Salmonella. “At first I thought, ‘that cannot be,”’ Elpers said. “I thought the proteomics was messed up, so we checked them.”
Elpers stained her cells grown in cooler temperatures for flagella proteins and looked under a 100x microscope. “I was quite excited when I did the staining and could see the flagella,” she said.
The team plans to look further into the flagella — it appears that they may be structured differently at cooler temperatures than at body temperature and may move differently. At body temperature, the team could see the Salmonella swimming around quickly, while at cooler temperatures the bacteria creep and crawl slowly.
“What is the flagella doing at the lower temperature?” asked Michael Hensel, the lead author. “The temperature is similar to conditions in agriculture — prior to climate change. It’s a bacterial pathogen that hasn’t been considered to be motile at that temp. But it may actually be able to reach new hosts and spread.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.
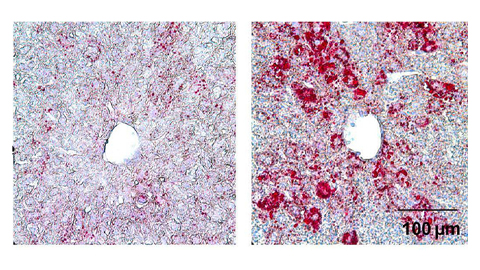
From the journals: JLR
How lipogenesis works in liver steatosis. Removing protein aggregates from stressed cells. Linking plasma lipid profiles to cardiovascular health. Read about recent papers on these topics.
Small protein plays a big role in viral battles
Nef, an HIV accessory protein, manipulates protein expression in extracellular vesicles, leading to improved understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis.

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.

