A mold’s dangerous responses to its environment
Aflatoxins are among the most dangerous of natural products. At a high dose, the toxins can cause fatal liver failure; at lower doses, by forming adducts with guanine bases in DNA, they can cause mutations that lead to liver cancer.

The toxins are made by filamentous fungi in the Aspergillus family found in soil and are able to colonize the grains and seeds that constitute many of the world's most important food crops. Aspergilli don't need aflatoxins to survive; they activate aflatoxin synthesis in response to environmental conditions, especially heat and moisture. Since hotter days are coming worldwide, researchers would like to find strategies to reduce aflatoxin production.
The genome of Aspergillus flavus, the chief culprit in introducing aflatoxin to human and animal food supplies, first was sequenced in 2006. But there's a difference between knowing what sequences are in a genome and knowing what they do; many sections of the A. flavus genome have not been annotated, meaning that researchers have had little insight into their function.
In a recent article in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, researchers at the Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University in China, led by Mingkun Yang, report on a proteogenomic analysis of A. flavus. By using the whole fungal genome instead of only its known coding sequences as the reference database to identify peptides detected through mass spectrometry, the team discovered over 700 new protein-coding genes.
"The authors provide a significant improvement to the genome annotation in Aspergillus and demonstrate the use of proteogenomics as a tool especially in organisms lacking high-quality genome annotations," one anonymous peer reviewer wrote.
Researchers cultured the fungus under cold, salty and oxidative stress conditions to maximize phenotypic variability, and they were rewarded: The fungi expressed a smorgasbord of proteoforms, including over 200 new-to-science splice variants, some single-amino-acid variants and a few unexpected intergenic peptides. In follow-up quantitative PCR experiments, the researchers observed that stressful conditions substantially affected the expression of some of the new genes.
Based on homology to other, better-annotated proteins in the literature, the authors think that they may have identified new metabolic enzymes, signaling proteins and stress response factors. They have not yet determined whether any of the new genes are involved in aflatoxin production.
According to the researchers, follow-up studies of the new protein-coding genes and when and where they are expressed may improve our understanding of when and why aflatoxin is produced.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
How a gene spurs tooth development
University of Iowa researchers find a clue in a rare genetic disorder’s missing chromosome.
New class of antimicrobials discovered in soil bacteria
Scientists have mined Streptomyces for antibiotics for nearly a century, but the newly identified umbrella toxin escaped notice.
New study finds potential targets at chromosome ends for degenerative disease prevention
UC Santa Cruz inventors of nanopore sequencing hail innovative use of their revolutionary genetic-reading technique.
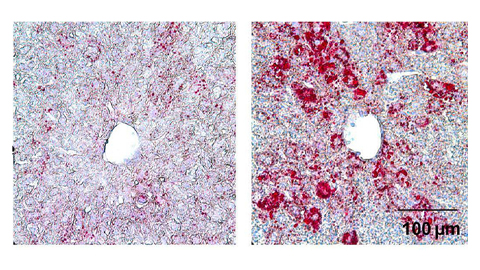
From the journals: JLR
How lipogenesis works in liver steatosis. Removing protein aggregates from stressed cells. Linking plasma lipid profiles to cardiovascular health. Read about recent papers on these topics.
Small protein plays a big role in viral battles
Nef, an HIV accessory protein, manipulates protein expression in extracellular vesicles, leading to improved understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis.

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.

